EnOS Device Connectivity and Management¶
EnOS Device Connectivity and Management aims to bridge the boundaries between the physical and digital worlds. It not only provides underlying communication capabilities but also helps you digitize your device assets from scratch through a complete workflow.
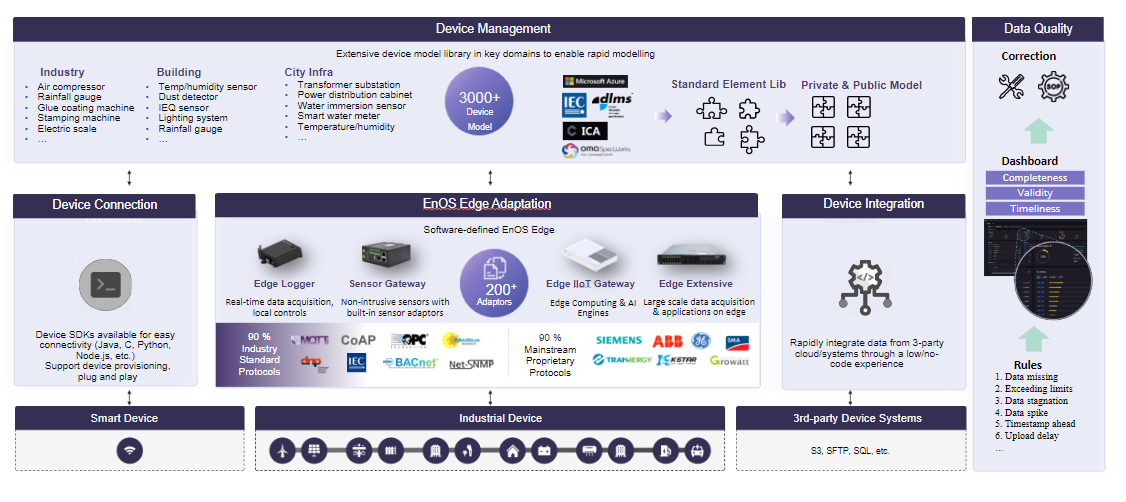
To achieve this goal, EnOS divides the device cloud migration process into five core stages: device modeling, device onboarding, device connection, device management, and device data quality monitoring.
Device Modelling¶
The first step in device connection is not connecting network cables, but defining the “thing”. In EnOS, assets with similar characteristics can be uniformly abstracted through modeling to build a universal model.
A model is an abstract description of a specific device asset or non-device asset (logical asset). It defines the object’s characteristics, capabilities, and services. EnOS supports model reuse through a public model library and provides model features based on industry standards such as IEC, ICA, and OMA to ensure data consistency across different devices and applications.
For more information, see Models and Asset Modeling.
Device Onboarding¶
After completing the model definition, you can quickly and accurately register and configure devices in the cloud using EnOS Device Onboarding.
EnOS Device Onboarding caters to multiple scenarios and domains, guiding you through the entire process from product creation and parameter configuration to authentication information generation. It not only simplifies the onboarding process but also incorporates a comprehensive onboarding quality control mechanism. Before the device establishes a physical connection, it verifies the correctness of the configuration, significantly reducing the risk of onboarding failure and ensuring a “successful onboarding” experience.
Device Connectivity¶
Once the device onboarding configuration is completed in the cloud, the physical device can establish an actual communication link with EnOS through a specific network protocol and begin transmitting data. EnOS supports three main connection methods to adapt to different hardware environments:
Direct Connection¶
Smart devices can connect to and communicate with EnOS directly through 3 device protocols, namely MQTT, HTTP, or CoAP, via Wi-Fi, GPRS, 3G, or 4G signals. Such devices include devices with smart acquisition rods, such as household inverters, and household energy storage batteries and smart home devices, such as surveillance cameras, and smart thermometers and hygrometers.
For more information, see Device and Data Connectivity.
Connection Through Gateway¶
Another way to connect devices to EnOS is through an edge gateway device. After a device is connected to the gateway, the gateway device communicates with EnOS based on the MQTT protocol. The device data are first collected by the edge gateway where the gateway serves as a proxy to help the devices complete operations such as login and data transmission. The device types that can connect to EnOS via this method include both smart devices and non-smart devices. Non-smart devices lack the ability to connect to EnOS via Wi-Fi, 3G, or 4G.
For more information, see Connecting Non-Smart Devices to EnOS Cloud via Edge.
Cloud-to-cloud¶
Certain devices might have already been onboarded or provisioned in an existing system or cloud, in this case, you can use EnOS Device Integration Service to design and build integration flows in a low code or no code manner to integrate device data across enterprises or organizations
For more information, see Device Data Integration Service.
Device Management¶
EnOS provides a full device lifecycle management as per your business needs, from the planning and design phase to the provisioning phase, servicing phase, maintenance phase, and finally the decommissioning phase.
For more information, see Device Lifecycle Management.
Device Data Quality¶
EnOS Device Data Quality monitors the quality of real-time data accessed from EnOS Device Connectivity & Management for completeness, validity, and timeliness based on configurable assessment rules and generates quality dashboards and reports to help enterprises easily assess data quality.
For more information, see Data Quality.