Edge Computing¶
Compared with centralized deployment of cloud computing, Edge computing not only solves the problems of excessive delay and excessive aggregated traffic, but also provides better support for real-time and bandwidth-intensive services.
Features of edge computing:
Low latency, edge computing focuses on real-time, short-period data analysis, which can better support the real-time intelligent processing and execution of local services;
More secure, the data in edge computing is only exchanged between the source data device and the edge device, and no longer uploads all to the cloud, preventing the risk of data leakage;
Relieve the flow pressure, filter and preprocess the data in advance at the edge to reduce the upload flow pressure; For model points, it is often necessary to do some preprocessing, or perform some simple calculations, which can be performed directly using the EnOS Edge computing module.
Application Scenario¶
EnOS Edge is committed to precipitating common algorithms for stream processing in the IoT field. Developers can complete the development, operation and maintenance of stream data processing tasks through configuration. In addition, the EnOS Edge computing service also provides a complete set of underlying encapsulated StreamSets operators for developers to develop customized stream data processing tasks to meet complex business needs.
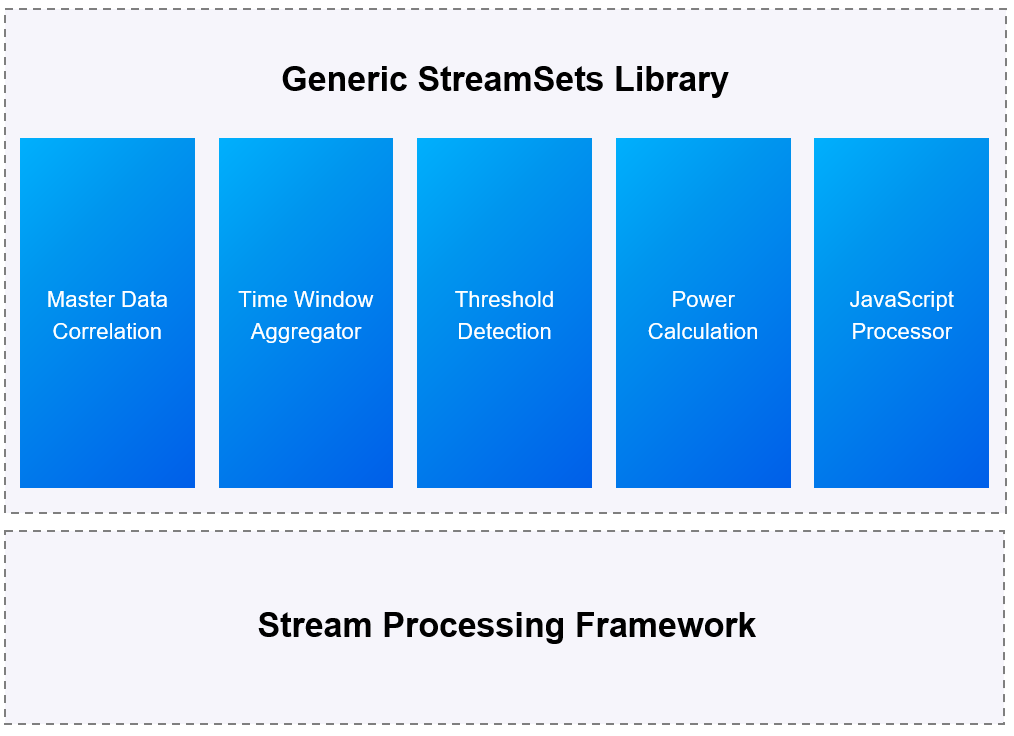
EnOS Edge computing service can be applied to the following scenarios:
Active power calculation of photovoltaic inverters, which supports the calculation of the 5-minute window average value of a single telemetry point of a single device;
The 10-minute average active power of the fan supports the calculation of the 10-minute window average value of a single telemetry point of a single device;
Equipment status statistics, according to the equipment status (remote communication point) to count the number of equipment in a certain state.
Features¶
Continuous real-time data stream¶
The data that the streaming data processing engine needs to process is real-time and continuous. The data stream is subscribed and consumed by the stream data processing service in chronological order. Data is generated continuously, so the data stream is continuously integrated into the stream data processing system. Therefore, streaming data is always real-time and continuous.
Continuous and efficient calculation¶
The computing mode of EnOS Edge computing service is “event triggered”. The trigger is the continuous stream data mentioned earlier. Whenever new streaming data is sent to the streaming data processing system, the system immediately starts and executes calculation tasks.
Real-time streaming data integration¶
After stream data triggers stream data processing, the calculation result is continuously recorded in the target data storage according to the pre-configured storage strategy.
Streaming data processing flow¶
Raw data processing: After the original data of the measuring point is collected by the protocol, it is converted into a model measuring point according to the point mapping template, and then sent to the edge computing module. Edge computing services filter data according to specified thresholds.
Data calculation: The data after threshold filtering is aggregated and calculated by the algorithm defined in the data processing strategy.
Output calculation result: The data processed by the streaming data processing module will flow into the downstream module, and will be recorded in the time series database (TSDB) or other target storage system according to the pre-configured storage strategy. Users can query the stored data through API.
StreamSets operator¶
EnOS Edge computing service provides a complete set of underlying encapsulated StreamSets operators for developers to develop customized stream data processing tasks based on business needs. For more information about the StreamSets operators supported by EnOS Edge, see The list of supported StreamSets operators.