Unit 4: Developing a Python Program to Enable RPi to Connect¶
After the device modeling and alert configurations are completed on the EnOS Management Console, you can connect the RPi to EnOS by using the EnOS Device SDK for MQTT for Python.
For detailed information about the EnOS Device SDK for MQTT for Python, refer to the readme file on GitHub.
Step 1: Setting Up Development Environment¶
EnOS Device SDK for MQTT for Python requires Python 2.7.12 or higher. Take the following steps to set up the development environment on RPi.
Run the following commands in the Terminal to install the requried libraries.
sudo apt-get install libffi-dev sudo apt-get install libssl-dev sudo apt-get install python-opencv
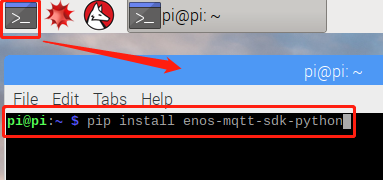
Run the following command in the Terminal to install the EnOS Device SDK.
pip install enos-device-sdk-python
Step 2: Programming for Connection¶
After the EnOS Device SDK for MQTT for Python is installed, take the following steps to connect the RPi device to EnOS Cloud (you can also refer to the code sample in the SDK readme file).
Develop a python program offline for connecting the RPi to EnOS. The program needs to include the following parts.
The directory that contains the python program and log files in the RPi system. For example:
cwd = '/home/pi/enos_device_demo/'
The host and port of the EnOS service. Contact your EnOS project manager for details if needed. For example:
enos_mqtt_url = "tcp://mqtt-{service_host}:{port}"
The keys and secrets of the product and devices, which are generated when registering the RPi device on the EnOS Management Console. For example:
product_key = "49vZUaG8" device_key = "CiwZTtAqRw" device_secret = "y6OtEzmkRViXcw1qdMYA"
Make sure the keys and secrets of the product, device, and sub-device, as well as the asset ID, are correct.
Copy the python program to the USB flash disk and plug it to the RPi. Next, copy the program to a folder of your choice.
The following sample is for your reference.
from message.upstream.status.SubDeviceLoginRequest import SubDeviceLoginRequest
from core.MqttClient import MqttClient
from message.upstream.topo.TopoAddRequest import TopoAddRequest
from message.upstream.topo.SubDeviceInfo import SubDeviceInfo
from message.upstream.tsl.MeasurepointPostRequest import MeasurepointPostRequest
from message.upstream.topo.TopoGetRequest import TopoGetRequest
from message.upstream.topo.TopoDeleteRequest import TopoDeleteRequest
from led import set_light, get_light
from concurrent.futures import ThreadPoolExecutor
from threading import current_thread
import random
import time
cwd = '/home/pi/enos_device_demo/'
enos_mqtt_url = "tcp://mqtt-{service_host}:{port}"
# gateway parameters
gateway_product_key = "NBXxeOUg"
gateway_device_key = "bTI4gHRvMw"
gateway_device_secret = "z8FwQzHg4DAOQQUfrpl4"
# sub-device parameters
sub_product_key = 'xxxx'
sub_device_key = "xxxx"
sub_device_secret = "xxxx"
sub_device_asset_id = 'xxxx'
def onOnline():
global connected
connected = True
print 'connected... %s' % connected
def onOffine():
print 'disconnected...'
def get_topo(mqtt_client):
try:
topo_get_req = TopoGetRequest.builder().build()
topo_get_res = mqtt_client.publish(topo_get_req)
print 'topo_response: code: %s' % topo_get_res.getCode()
print topo_get_res.getData()
except Exception as e:
print e
def add_topo(mqtt_client):
try:
topo_req = TopoAddRequest.builder().addSubDevice(SubDeviceInfo(sub_product_key, sub_device_key, sub_device_secret)).build()
topo_res = mqtt_client.publish(topo_req)
print 'topo_response: code: %s' % topo_res.getCode()
print 'topo_response: message: %s' % topo_res.getMessage()
except Exception as e:
print e
def delete_topo(mqtt_client):
try:
topo_del_req = TopoDeleteRequest.builder().addSubDevice(sub_product_key, sub_device_key).build()
topo_del_res = mqtt_client.publish(topo_del_req)
print 'topo_delete_response: %s' % topo_del_res.getCode()
except Exception as e:
print e
def login_sub_device(mqtt_client):
try:
login_req = SubDeviceLoginRequest.builder().setSubDeviceInfo(sub_product_key, sub_device_key, sub_device_secret).build()
login_res = mqtt_client.publish(login_req)
print 'login_response: code: %s' % login_res.getCode()
print 'login_response: message: %s' % login_res.getMessage()
except Exception as e:
print e
# post measuring points data via MQTT
def post_measure_points(mqtt_client, timestamp):
try:
meapt_req = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder() \
.setProductKey(sub_product_key).setDeviceKey(sub_device_key) \
.addMeasurePoint('Temperature', random.randint(10, 30)) \
.addMeasurePoint('Humidity', random.randint(0, 100)) \
.setTimestamp(timestamp) \
.build()
meapt_res = mqtt_client.publish(meapt_req)
print 'measurepointPost_response: %s' % meapt_res.getCode()
except Exception as e:
print e
# handle the received downstream message and implement your logic
def handle_msg(arrivedMessage, replyHandler):
'''
:param arrivedMessage: <attributes:deviceKey,prodectKey,id,messageTopic,method,params,version>
:param replyHandler: <method:replyWithPayload>
'''
# handle logic
global thread_id
thread_id = current_thread().ident
print(arrivedMessage.params)
signal = str(arrivedMessage.params.get('Light'))
if signal == '0':
set_light(signal)
replyHandler.reply_with_payload(code=200, message='success', data=thread_id)
elif signal == '1' or signal == '2':
executor.submit(light_thread, signal, thread_id)
replyHandler.reply_with_payload(code=200, message='success', data=thread_id)
def light_thread(signal, threadID):
while threadID == thread_id:
if signal == '1':
state = int(get_light())
set_light(signal) if state == 0 else None
time.sleep(0.1)
elif signal == '2':
current_sig = str(1 - int(get_light()))
set_light(current_sig)
time.sleep(5)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print 'main begin...'
client = MqttClient(enos_mqtt_url, gateway_product_key, gateway_device_key, gateway_device_secret)
client.setupFileLogger(cwd + 'log.json') # set the log configuration in the SDK
client.onOnline = onOnline
client.onOffline = onOffine
print 'try to connect'
connected = False
connect_cnt = 0
while connected is False:
client.connect() # connect in sync
print 'connecte status %s' % connected
connect_cnt += 1
print 'connect for %d time' % connect_cnt
print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime(time.time()))
time.sleep(10)
print 'connect finished'
thread_id = None
executor = ThreadPoolExecutor(1)
client.onMessage(handle_msg) # register the handle_msg
add_topo(client) # add the device to the gateway as sub-device
login_sub_device(client) # login the sub-device
cnt = 0
interval = 1
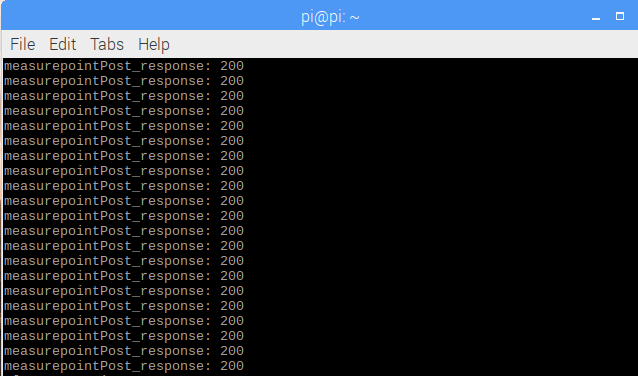
while True:
timestamp = int(time.time() * 1000) # timestamp in milliseconds
post_measure_points(client, timestamp) # publish measuring points data
time.sleep(interval)
cnt = cnt + 1
Note
In this sample, the LED light control signal and status signal are real physical signals, and the humidity and temperature data is simulated.
Step 3: Running the Program for Connection¶
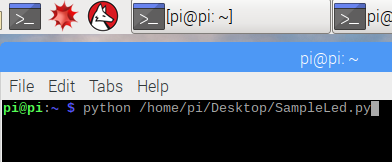
Take the following steps to run the program.
In the Terminal, run the python program.
Check the running status of the program. The measurement point data will start to upload to EnOS Cloud.