Unit 5: Controlling the Data Upload Interval¶
The control service defined in the computer model enables you to control the PC system to EnOS Cloud data upload interval (frequency).
In this unit, you will add the service handler function to the program that is used in Unit 4.
Declare the function
handleServiceInvocation()for handling the service invocation.public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); handleServiceInvocation(); updateAttribute(); monitor(); }
Program the
handleServiceInvocation()function for handling the commands that are issued from EnOS Cloud.public static void handleServiceInvocation() { IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply> handler = new IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply>() { @Override public ServiceInvocationReply onMessage(ServiceInvocationCommand request, List<String> argList) throws Exception { System.out.println("<<<<< [service command] rcvn async service invocation command: " + request + " topic: " + argList); if (request.getMessageTopic().contains("control")) { Map params=request.getParams(); interval= (int) params.get("interval"); } return ServiceInvocationReply.builder() .addOutputData("result", 0) .build(); } }; client.setArrivedMsgHandler(ServiceInvocationCommand.class, handler); }
Compile and run the program for device connection, data ingestion, and service handling.
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.ConnCallback; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.MqttClient; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.msg.IMessageHandler; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.downstream.tsl.ServiceInvocationCommand; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.downstream.tsl.ServiceInvocationReply; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.upstream.tsl.*; import oshi.hardware.HardwareAbstractionLayer; import oshi.software.os.OperatingSystem; public class Sample { private static final String uri = "tcp://{host}:{port}"; private static final String productKey = "product_key"; private static final String deviceKey = "device_key"; private static final String deviceSecret = "device_secret"; private static MqttClient client; private static int interval=5; // 10s public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); handleServiceInvocation(); updateAttribute(); monitor(); } // Device connection initialization public static void connect() { System.out.println("start connect with callback ... "); try { client = new MqttClient(uri, productKey, deviceKey, deviceSecret); client.getProfile().setConnectionTimeout(60).setAutoReconnect(true); client.connect(new ConnCallback() { @Override public void connectComplete(boolean reconnect) { System.out.println("connect success"); } @Override public void connectLost(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectLost"); } @Override public void connectFailed(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectFailed : " + cause); } }); } catch (Throwable var1) { } System.out.println("connect result :" + client.isConnected()); } // Ingesting PC system and hardware data public static Map<String, Object> collectDeviceInfo() { oshi.SystemInfo si = new oshi.SystemInfo(); HardwareAbstractionLayer hal = si.getHardware(); OperatingSystem os = si.getOperatingSystem(); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<String, Object>(); data.put("system", os.toString()); data.put("model", hal.getComputerSystem().getManufacturer() + " " + hal.getComputerSystem().getModel()); data.put("cpu_core", hal.getProcessor().getLogicalProcessorCount()); data.put("cpu_used", hal.getProcessor().getSystemCpuLoad()); data.put("mem_total", hal.getMemory().getTotal()); data.put("mem_used", hal.getMemory().getAvailable()); data.put("cpu_used_average", hal.getProcessor().getSystemLoadAverage()); data.put("cpu_temperature", hal.getSensors().getCpuTemperature()); return data; } // Updating PC attributes with the ingested system and hardware data public static void updateAttribute(){ Map<String, Object> deviceInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); System.out.println("Computer info: "+deviceInfo); AttributeUpdateRequest request = AttributeUpdateRequest.builder() .setQos(1) .addAttribute("system", deviceInfo.get("system")) .addAttribute("model", deviceInfo.get("model")) .addAttribute("cpu_core", deviceInfo.get("cpu_core")) .addAttribute("mem_total", deviceInfo.get("mem_total")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Update Attribute: "+request); try { AttributeUpdateResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Uploading PC system data to EnOS Cloud public static void postMeasurepoint(Map<String, Object> systemInfo) { MeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .addMeasurePoint("cpu_used", Double.parseDouble(systemInfo.get("cpu_used").toString())+0.0) .addMeasurePoint("mem_used", systemInfo.get("mem_used")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Measurepoint: "+request); try { MeasurepointPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Monitoring the CPU load public static void monitor() throws Exception { long lastReportTs=0; while (true) { Map<String, Object> systemInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); postMeasurepoint(systemInfo); double cpu_load= (double) systemInfo.get("cpu_used"); if (cpu_load>0.2) { long ts = System.currentTimeMillis(); if ((ts-lastReportTs)>(60*1000)) { lastReportTs=ts; reportCPULoadEvent(cpu_load, "[Warning] CPU load: "+ cpu_load); }else{ System.out.println("[Warning] No reporting required, CPULoadEvent: " + cpu_load); } } Thread.sleep(interval*1000); } } // Reporting CPU load events public static void reportCPULoadEvent(double value, String describe) { EventPostRequest request=EventPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .setEventIdentifier("cpu_event") .addValue("value", value) .addValue("message", describe) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Event: "+request); try { EventPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Handling service invocation public static void handleServiceInvocation() { IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply> handler = new IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply>() { @Override public ServiceInvocationReply onMessage(ServiceInvocationCommand request, List<String> argList) throws Exception { System.out.println("<<<<< [service command] rcvn async service invocation command: " + request + " topic: " + argList); if (request.getMessageTopic().contains("control")) { Map params=request.getParams(); interval= (int) params.get("interval"); } return ServiceInvocationReply.builder() .addOutputData("result", 0) .build(); } }; client.setArrivedMsgHandler(ServiceInvocationCommand.class, handler); } }
Go to EnOS Management Console and click Monitoring and Maintenance > Online Debugging.
Select Computer for Product and PC_Win10 for Device.
Go to the Real Device tab, click Invoke Service, and select contol(control) from the Feature drop-down. Enter a value for
interval(for example, 10) and click Send Command.The processing status of the command will be shown under the Commands tab at the Device Details page.
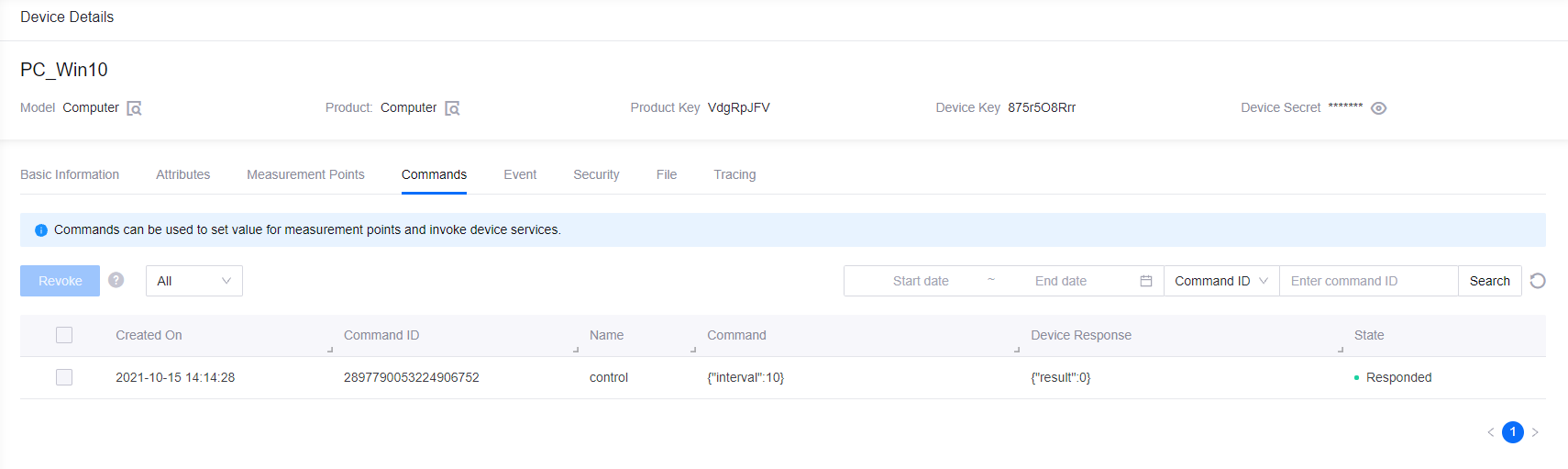
The new data upload interval will be shown under the Measurement Points tab at the Device Details page (with “Real-time Update” enabled).