Edge Cascading¶
Modern industry has a series of standards and compliance requirements, such as the IEC 62264 standard, ISA-95 standard, the China Electricity Regulatory Commission issued the “Power Monitoring System Safety Protection Regulations”, “Power Monitoring System Safety Protection Master Plan”. In these networks, only the top layer has connectivity to the cloud and the lower layers in the hierarchy can only communicate with adjacent north and south layers.
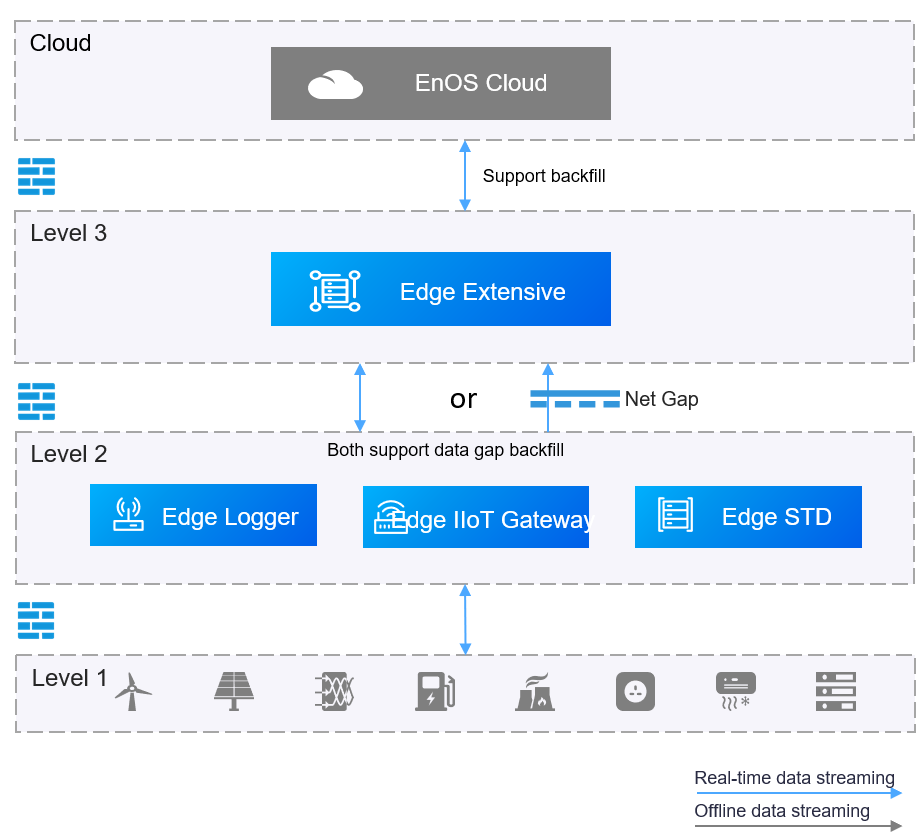
EnOS Edge provides multi-tier edge cascading function to meet the requirements of these standards. Meanwhile, each layer can implement edge or fog computing for its own business requirements and provide interoperability services (e.g. aggregation, filtering, analysis, etc.) for the upper layer.
The architecture of EnOS Edge Cascading is as follows:
Application¶
You can choose the following methods to configure cascading according to the scenarios:
Configuration Method |
Cloud Cascade Configuration |
Local Cascade Configuration |
|---|---|---|
Scenario |
Centrally manage upper and lower Edge devices in the Cloud Asset Configuration tool, and use the Cloud Cascade Configuration Tool to quickly configure Edge Cascade |
Separately manage upper and lower Edge devices in the cloud and the local Edge management tool and configure Edge cascading by using the two tools together. |
Advantage |
Centrally manage assets in the cloud for faster provisioning |
Network disconnection scenario, fewer dependency |
Recommended index |
☆☆☆☆☆ |
☆☆☆ |
Real-time data cascade & data backfill |
√ |
√ |
File cascade |
√ |
√ |
Control Cascade |
√ |
√ |
Direct network connection & Cross Net Gap |
√ |
√ |
Automatically split connections based on the number of cascading points |
√ |
√ |
Open modification of the upper-level Edge cascade access mapping formula |
√ |
√ |
Cascade connection version inconsistency, suspension of forwarding |
√ |
√ |
Select cascading forwarding points as needed |
√ |
× |
Select mapped access model points with one click |
√ |
× |
Remotely debug Zone 1 devices in the cloud |
√ |
× |
Features¶
Supports multi-tier cascading and multiple configuration centers collaboration to configure edge cascading.
Support real-time data upstream cascading, collect and aggregate telemetry
Support control commands downstream cascading.
Support cascading cross the net gap.
Support automatic tag configuration.
Data gap backfill is supported between adjacent Edge devices.
Key Concepts¶
Cross Net-Gap Service¶
For scenarios with strict isolation requirements, air gaps are usually used as network isolators for security isolation between the networks of different security levels. For example, in the power sector, high-to-low and low-to-high air gaps are deployed between Security Zone I and Security Zone III.
Even if high-to-low or low-to-high air gap is deployed, EnOS Edge can still achieve data communication and file transfers between different security zones by transmitting data across the air gap, providing data exchange services for the deployed applications while conforming to on-site security regulations.