单元 5: 控制数据上传间隔¶
使用计算机模型中定义的 control 服务,你可以控制将 PC 系统数据上传到 EnOS Cloud 的间隔(频率)。
在本单元中,更新 单元4 中使用的程序以添加服务处理程序。
声明函数
handleServiceInvocation(),以处理服务调用。public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); handleServiceInvocation(); updateAttribute(); monitor(); }
编写
handleServiceInvocation()函数,以处理从 EnOS Cloud 发出的命令。参考以下代码示例:public static void handleServiceInvocation() { IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply> handler = new IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply>() { @Override public ServiceInvocationReply onMessage(ServiceInvocationCommand request, List<String> argList) throws Exception { System.out.println("<<<<< [service command] rcvn async service invocation command: " + request + " topic: " + argList); if (request.getMessageTopic().contains("control")) { Map params=request.getParams(); interval= (int) params.get("interval"); } return ServiceInvocationReply.builder() .addOutputData("result", 0) .build(); } }; client.setArrivedMsgHandler(ServiceInvocationCommand.class, handler); }
编译并运行程序以进行设备连接、数据采集、和服务处理。参考以下程序代码示例:
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.ConnCallback; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.MqttClient; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.exception.EnosException; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.core.msg.IMessageHandler; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.downstream.tsl.ServiceInvocationCommand; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.downstream.tsl.ServiceInvocationReply; import com.enosiot.enos.iot_mqtt_sdk.message.upstream.tsl.*; import oshi.hardware.HardwareAbstractionLayer; import oshi.software.os.OperatingSystem; public class Sample { private static final String uri = "tcp://{host}:{port}"; private static final String productKey = "product_key"; private static final String deviceKey = "device_key"; private static final String deviceSecret = "device_secret"; private static MqttClient client; private static int interval=5; // 10s public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { connect(); handleServiceInvocation(); updateAttribute(); monitor(); } // Device connection initialization public static void connect() { System.out.println("start connect with callback ... "); try { client = new MqttClient(uri, productKey, deviceKey, deviceSecret); client.getProfile().setConnectionTimeout(60).setAutoReconnect(true); client.connect(new ConnCallback() { @Override public void connectComplete(boolean reconnect) { System.out.println("connect success"); } @Override public void connectLost(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectLost"); } @Override public void connectFailed(Throwable cause) { System.out.println("onConnectFailed : " + cause); } }); } catch (Throwable var1) { } System.out.println("connect result :" + client.isConnected()); } // Ingesting PC system and hardware data public static Map<String, Object> collectDeviceInfo() { oshi.SystemInfo si = new oshi.SystemInfo(); HardwareAbstractionLayer hal = si.getHardware(); OperatingSystem os = si.getOperatingSystem(); Map<String, Object> data = new HashMap<String, Object>(); data.put("system", os.toString()); data.put("model", hal.getComputerSystem().getManufacturer() + " " + hal.getComputerSystem().getModel()); data.put("cpu_core", hal.getProcessor().getLogicalProcessorCount()); data.put("cpu_used", hal.getProcessor().getSystemCpuLoad()); data.put("mem_total", hal.getMemory().getTotal()); data.put("mem_used", hal.getMemory().getAvailable()); data.put("cpu_used_average", hal.getProcessor().getSystemLoadAverage()); data.put("cpu_temperature", hal.getSensors().getCpuTemperature()); return data; } // Updating PC attributes with the ingested system and hardware data public static void updateAttribute(){ Map<String, Object> deviceInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); System.out.println("Computer info: "+deviceInfo); AttributeUpdateRequest request = AttributeUpdateRequest.builder() .setQos(1) .addAttribute("system", deviceInfo.get("system")) .addAttribute("model", deviceInfo.get("model")) .addAttribute("cpu_core", deviceInfo.get("cpu_core")) .addAttribute("mem_total", deviceInfo.get("mem_total")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Update Attribute: "+request); try { AttributeUpdateResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Uploading PC system data into EnOS Cloud public static void postMeasurepoint(Map<String, Object> systemInfo) { MeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .addMeasurePoint("cpu_used", Double.parseDouble(systemInfo.get("cpu_used").toString())+0.0) .addMeasurePoint("mem_used", systemInfo.get("mem_used")) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Measurepoint: "+request); try { MeasurepointPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Monitoring the CPU load public static void monitor() throws Exception { long lastReportTs=0; while (true) { Map<String, Object> systemInfo= collectDeviceInfo(); postMeasurepoint(systemInfo); double cpu_load= (double) systemInfo.get("cpu_used"); if (cpu_load>0.2) { long ts = System.currentTimeMillis(); if ((ts-lastReportTs)>(60*1000)) { lastReportTs=ts; reportCPULoadEvent(cpu_load, "[Warning] CPU load: "+ cpu_load); }else{ System.out.println("[Warning] No reporting required, CPULoadEvent: " + cpu_load); } } Thread.sleep(interval*1000); } } // Reporting CPU load events public static void reportCPULoadEvent(double value, String describe) { EventPostRequest request=EventPostRequest.builder() .setQos(0) .setEventIdentifier("cpu_event") .addValue("value", value) .addValue("message", describe) .build(); System.out.println(">>> Post Event: "+request); try { EventPostResponse resp = client.publish(request); System.out.println("<-- " + resp); } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } // Handling service invocation public static void handleServiceInvocation() { IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply> handler = new IMessageHandler<ServiceInvocationCommand, ServiceInvocationReply>() { @Override public ServiceInvocationReply onMessage(ServiceInvocationCommand request, List<String> argList) throws Exception { System.out.println("<<<<< [service command] rcvn async service invocation command: " + request + " topic: " + argList); if (request.getMessageTopic().contains("control")) { Map params=request.getParams(); interval= (int) params.get("interval"); } return ServiceInvocationReply.builder() .addOutputData("result", 0) .build(); } }; client.setArrivedMsgHandler(ServiceInvocationCommand.class, handler); } }
登录 EnOS 管理控制台,点击 设备监控 > 在线调试。
在 产品 下拉框中选择 Computer,然后在 设备 下拉框中选择 PC_Win10。
在 调试真实设备 下,点击 服务调用,接着在 调试功能 下拉框选择 contol(control) 并为
interval填写一个值(例如,10)。点击 发送指令。点击进入 设备详情 > 命令 页面,查看命令运行状态。
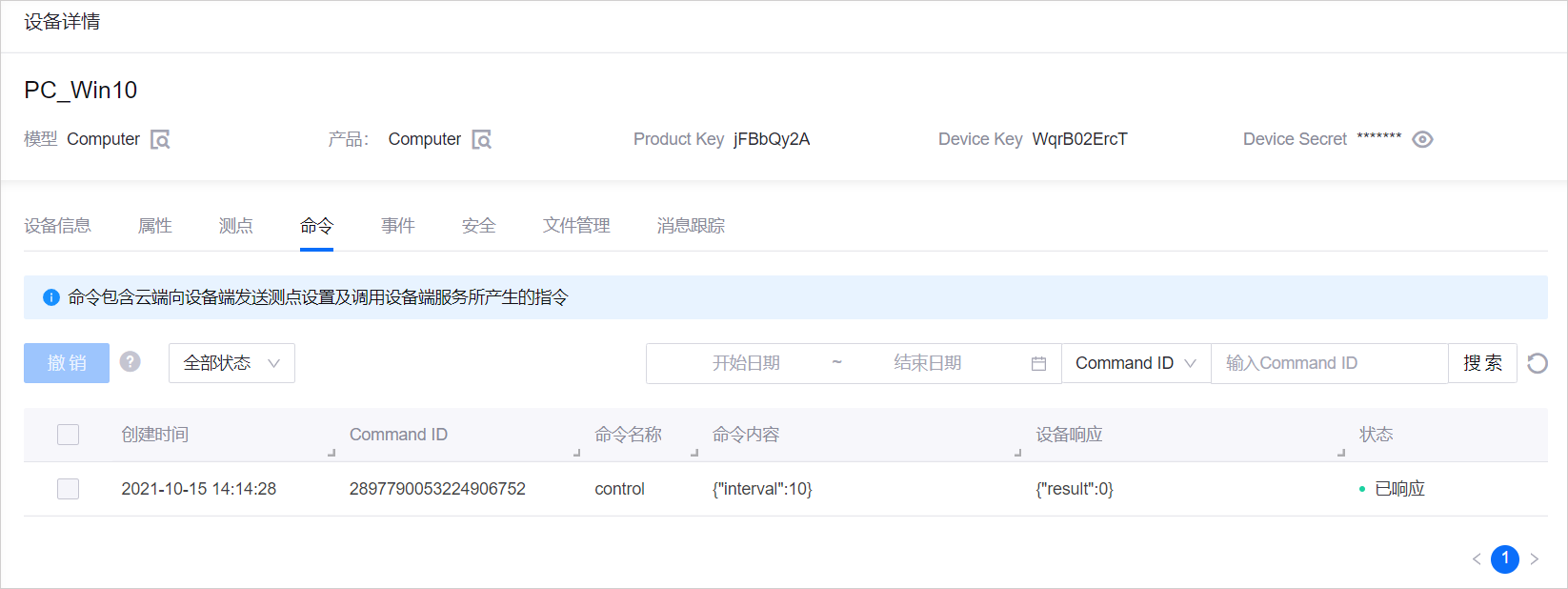
点击进入 设备详情 > 测点 页面,查看更新后的数据上传间隔(启用 “实时刷新”)。