Setting the Alert Triggering Delay Timer¶
In some scenarios, alerts need to be delayed until a specified time instead of triggering immediately when there is an anomaly.
Let us take the example of using EnOS to monitor the load factor of an electricity producing installation: when the load factor is over 120% for, say, 120 minutes, EnOS will then trigger the “Overload” alert. The alert triggering delay timer can be used in this scenario.
Concepts¶
Anomaly : When the measurement point data sent from a device satisfies the condition set in the alert rule, an anomaly is generated.
Alert triggering delay : The time from when an anomaly occurs to when the alarm is triggered.
Usage Notes¶
Start and End of Alert Triggering Delay¶
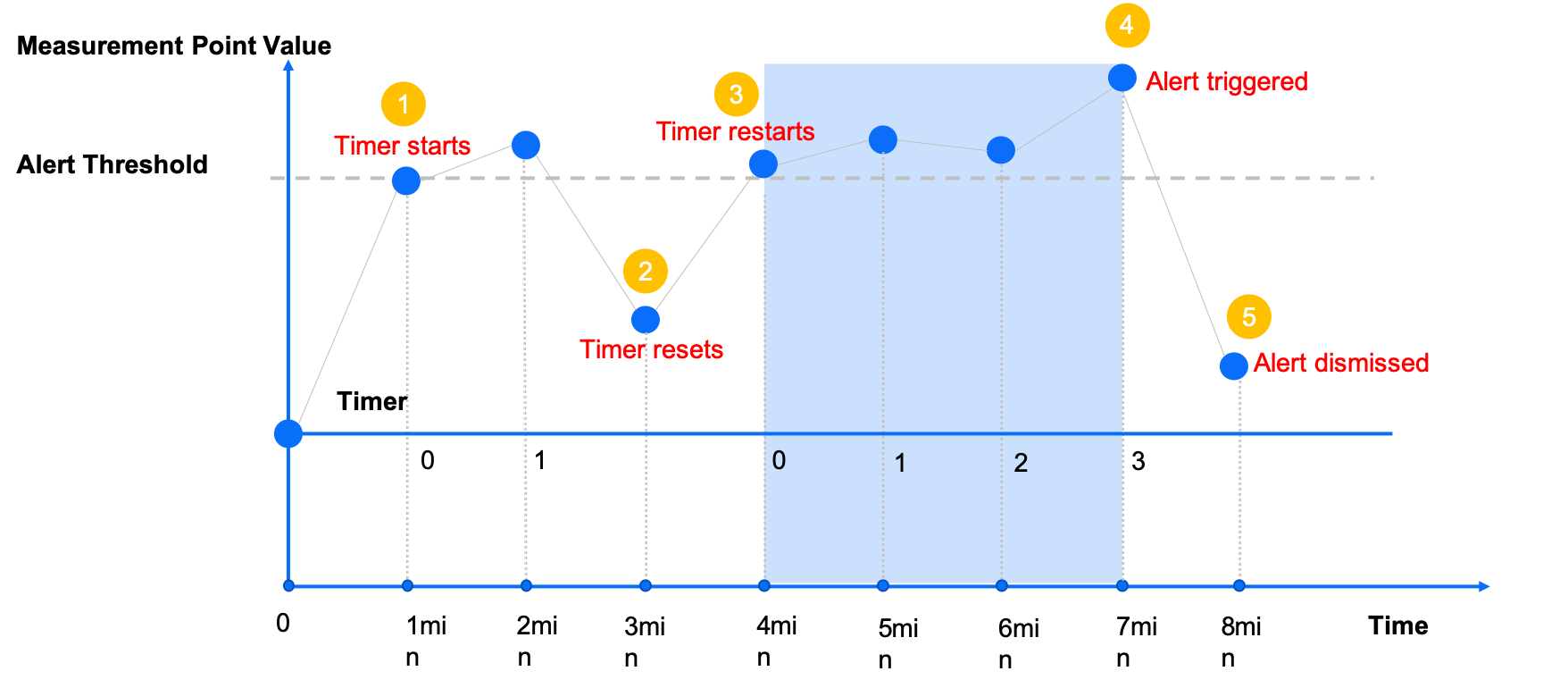
The following illustrate describes the process of delayed alarms with a delay time of 3 minutes as an example. The alarm can be delayed for up to 24 hours.
Timer starts: The delay timer starts the moment an anomaly is generated. As the following illustrates, the timer kicks off at 1min, as the measurement point value meets the condition of the alert rule. At 2 min, the anomaly persists, and the timer count increases by 1 minute.
Timer resets: If the anomaly is recovered before the timer times out, the timer is reset. As the following illustrates, the timer is reset to 0 minute at 3 min when the anomaly disappears.
Timer restarts: At 4 min, the anomaly reappears, and the timer restarts from 0 minute.
Alert triggered: At 7 min, the timer reaches 3 minutes and times out. An alert is triggered.
Alert dismissed: At 8 min, the anomaly disappears and the alert is dismissed.
About This Task¶
This task shows how to use the alert triggering delay function in a smart-building scenario. For details of this scenario, see Setting Different Alert Thresholds for Devices of the Same Model. For this task, we will use only the code snippet of the fridge ammeter.
Prerequisites¶
Ensure that you have the access to the model, asset management, and alert services. If not, contact your OU administrator. For more information, see Policies, Roles, and Permissions.
Go through the Setting Different Alert Thresholds for Devices of the Same Model.
Procedure¶
Select Alert Engine > Alert Rules. Create a new rule as per the following and set Alert Triggering Delay to
60seconds and click Confirm. For how to create an alert rule, see Creating Alert Rules.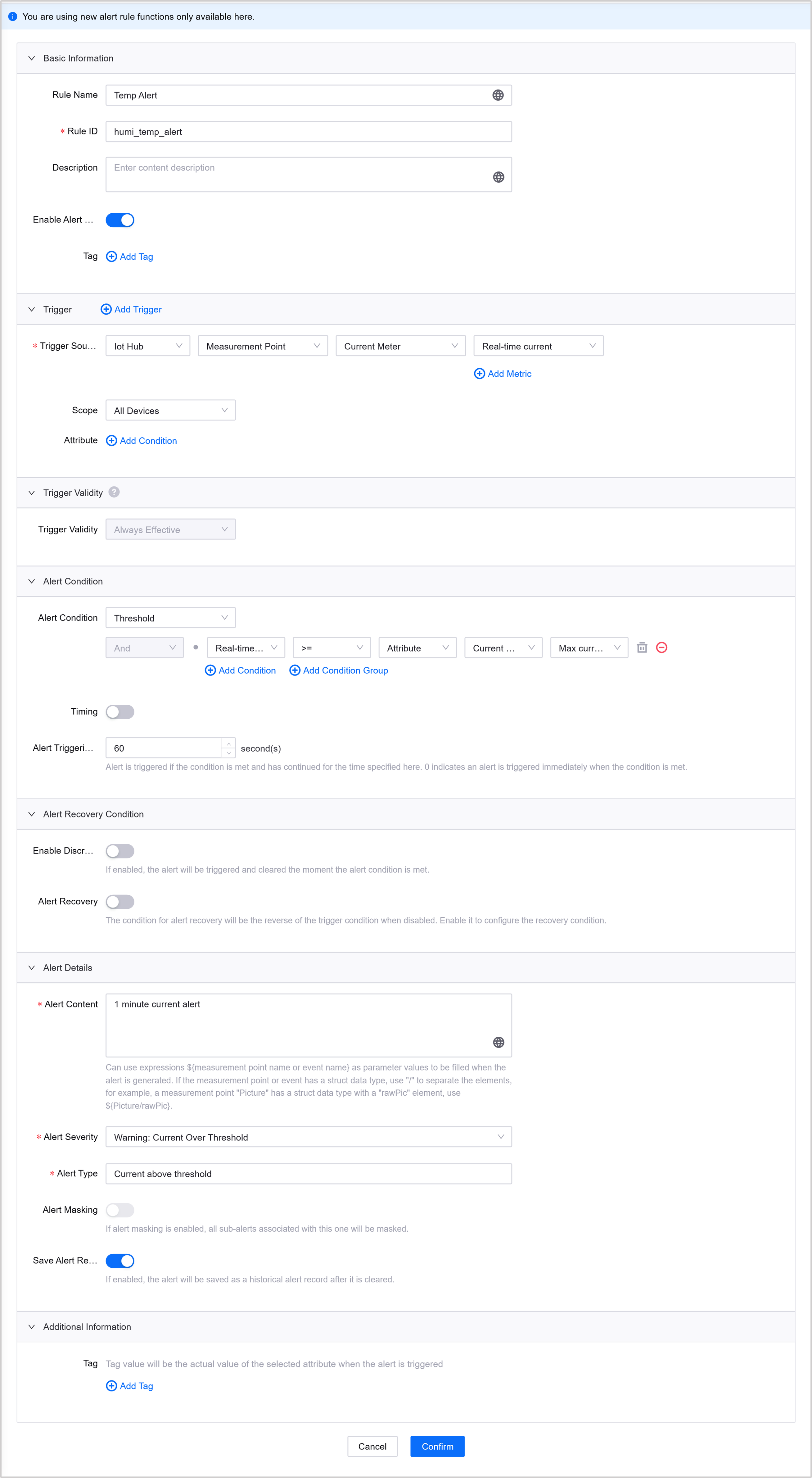
Copy the sample code
fridgeMQTTfrom Setting Different Alert Thresholds for Devices of the Same Model to your IDE and make the following changes:Change
MeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder().addMeasurePoint("rt_current", random.nextDouble() * 1500).build()toMeasurepointPostRequest request = MeasurepointPostRequest.builder().addMeasurePoint("rt_current", random.nextDouble() + 1500 ).build()so that the telemetric data Real-time current sent from the simulated ammeter exceeds theMax Current Allowed, thus generating the anomaly.Change
Thread.sleep(10000L)toThread.sleep(30000L)so that the simulated ammeter sends telemetry every 30 seconds. In this way, if the ammeter sends 3 consecutiveReal-time current, which is above theMax Current Allowed, to EnOS, the Temp Alert rule will be triggered.
Run
fridgeMQTT.
Results¶
Select Alert Engine > Alert Records. Once the ammeter sends 3 consecutive data to EnOS, which are all above the threshold, across 60 seconds, you will be able to see the triggered alert.
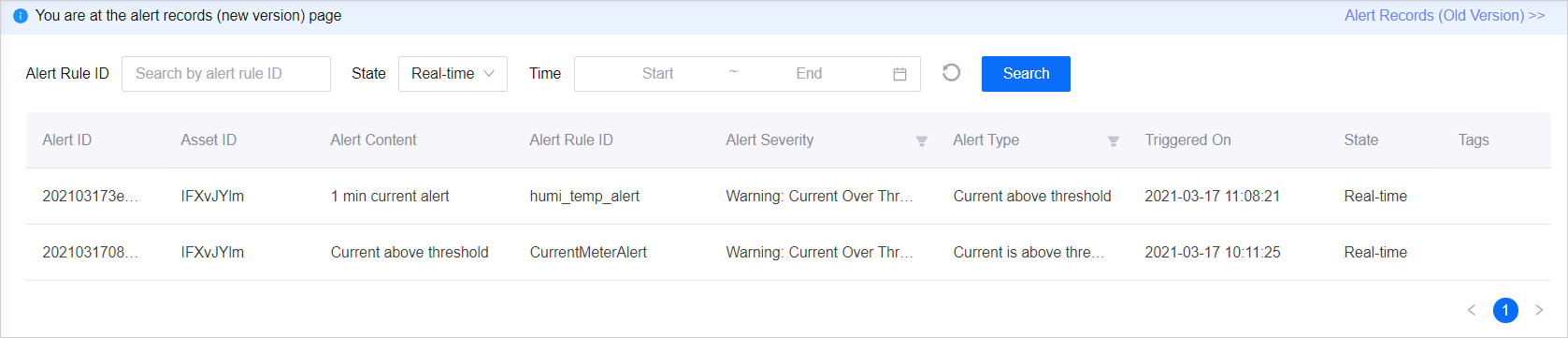
You can also call an API to query the triggered alerts, where the measurement point data value included in the response is the telemetric value when the timer starts timing.